The type of limestone is dependent on the NomenclatureAl : Aluminium What is "pH"pH refers to a range of values from 0 to 14 that measure the acidity or alkalinity of water or soil. Zero is the most acid and 14 is the most alkaline. Pure water is considered neutral with a pH of 7. Lime is alkaline, while plant and microbial growth and nitrogen fertilizers produce acid. Adding lime to acidic soil causes the soil's pH to rise from acidic toward alkaline, or from pH 5 to pH 7, for example. Most crops grow best at the mid-point of the pH range. However, potatoes are often grown at the lower end, while cabbages are grown at the higher end to control certain diseases such as scab or club root. Lime is fed into the primary crusher at
|
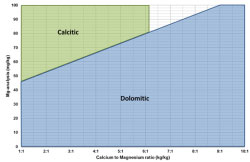
TechnicalTypes of limestoneThe word "lime" refers to products derived from burnt (calcined) limestone, such as quicklime and hydrated lime. Limestone is a naturally occurring and abundent sedimentary rock consisting of high levels of calcium and/or magnesium carbonate, and/or dolomite (calcium and magnesium carbonate), along with small amounts of other minerals. It is extracted from quarries and underground mines all over the world. Lime and limestone products are among the oldest materials used by humans for a very diverse range of applications. Today these products serve as an essential building block in every industrial process. The type of limestone is dependent on the Ca:Mg ratio and the Mg content of the lime. Dolomitic limestone consists of 35 to 46% magnesium carbonate. Magnesian limestone consists of 5 to 35% magnesium carbonate. High calcium limestone contains less than 5% magnesium carbonate Conversion TablesThe results from laboratory analysis of lime will not be presented in the same way. It is sometimes necessary to convert the analysis from various lime sources to the same component. This can be done making use of the conversion table below:
The water treatment industry makes use of not only lime but a variety of chemicals to achieve the desired pH of the water. The cost effectiveness of various compounds can be compared making use of the table below, permitted the process allow the substitution.
From the table it is evident that for every 1-ton of CaO a total of 1.78t of CaCO₃ is required to neutralise the same amount of product. In most instances the CaCO₃ will be significantly cheaper that the CaO and the process and transport will the determining factors in selecting the most cost effective solution. Neutralising Capacity of different lime and water treatment chemicalsIn practise liming material is not pure and contains various impurities that impact on the neutralising capacity thereof. The Calcium Carbonate Equivalent (CCE) is used to indicate the potential acid neutralisation capacity against that of pure CaCO₃. The relative neutralising capacity of different liming materials is given below:
Sieve Standards
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






 The ASTM E11-09e1 standards covers the requirements for design and construction of testing sieves using a medium of woven wire cloth mounted in a frame for use in testing for the classification of materials according to designated particle size and wire cloth meeting the specifications specified, to be designated test grade wire cloth.
The ASTM E11-09e1 standards covers the requirements for design and construction of testing sieves using a medium of woven wire cloth mounted in a frame for use in testing for the classification of materials according to designated particle size and wire cloth meeting the specifications specified, to be designated test grade wire cloth.